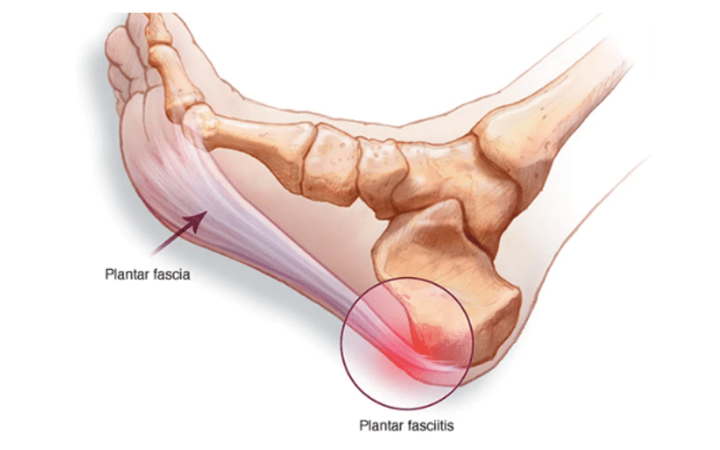
 Plantar
fasciitis is a common foot condition involving pain and inflammation in the
plantar fascia—a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot,
connecting the heel bone to the toes. It is one of the most frequent causes of
heel pain.
Plantar
fasciitis is a common foot condition involving pain and inflammation in the
plantar fascia—a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot,
connecting the heel bone to the toes. It is one of the most frequent causes of
heel pain.
Causes of
Plantar Fasciitis:
- Overuse: Repeated strain from
activities like running, walking, or standing can lead to inflammation of
the plantar fascia.
- Foot mechanics: Individuals
with flat feet or high arches may experience added stress on the plantar
fascia, increasing the likelihood of injury.
- Tight calf muscles: Tightness
in the calf muscles can place additional tension on the plantar fascia.
- Obesity: Excess body weight
puts extra pressure on the feet, contributing to the development of
plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
of Plantar Fasciitis:
- Sharp heel pain or pain along
the bottom of the foot, particularly noticeable with the first steps in
the morning or after periods of rest.
- Pain that improves with movement
but may worsen after extended activity.
- Tenderness and swelling in
the heel area.
Treatment
of Plantar Fasciitis:
- Rest: Reduce or avoid
activities that exacerbate the pain to allow for healing.
- Stretching Exercises:
Regularly stretch the calf muscles and plantar fascia to relieve tension
and reduce pain.
- Supportive Footwear: Wear
shoes with proper arch support and cushioning to alleviate pressure on the
plantar fascia.
- Orthotic Inserts: Use shoe
inserts or orthotics for added support and to promote even pressure
distribution.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice to the
affected area to reduce inflammation and ease discomfort.
 Plantar
fasciitis is a common foot condition involving pain and inflammation in the
plantar fascia—a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot,
connecting the heel bone to the toes. It is one of the most frequent causes of
heel pain.
Plantar
fasciitis is a common foot condition involving pain and inflammation in the
plantar fascia—a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot,
connecting the heel bone to the toes. It is one of the most frequent causes of
heel pain.