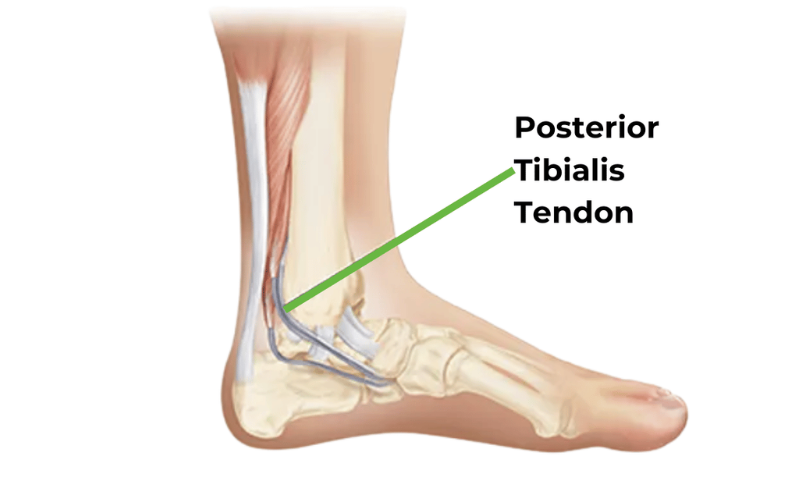
 Posterior
Tibial Tendonitis, commonly known as Post-Tib Tendonitis, is a condition characterized
by inflammation or irritation of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon runs
along the inner side of the ankle and foot, playing a vital role in supporting
the arch and stabilizing the foot during activities like walking and running.
Posterior
Tibial Tendonitis, commonly known as Post-Tib Tendonitis, is a condition characterized
by inflammation or irritation of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon runs
along the inner side of the ankle and foot, playing a vital role in supporting
the arch and stabilizing the foot during activities like walking and running.
Causes of
Post-Tib Tendonitis:
- Overuse or Repetitive Strain:
Activities that exert excessive stress on the posterior tibial tendon,
such as running, walking on uneven surfaces, or participating in
high-impact sports, can lead to tendonitis over time.
- Foot Structure Abnormalities:
Individuals with flat feet or other structural issues may be more
susceptible to developing Post-Tib Tendonitis.
- Footwear: Wearing ill-fitting
or unsupportive shoes can contribute to the onset of this condition.
- Age: Tendons generally become
less flexible and more prone to injury with age, making older individuals
more vulnerable to this condition.
Symptoms
of Post-Tib Tendonitis:
- Pain and Tenderness:
Discomfort along the inner side of the ankle and foot, typically near the
arch.
- Swelling and Redness:
Noticeable swelling and redness in the affected area.
- Difficulty Walking:
Challenges in walking, particularly on uneven surfaces or stairs.
- Arch Flattening: The arch of
the foot may flatten, or the foot may roll inward (overpronation).
- Weakness: Weakness in the
foot and ankle may occur.
Treatment
of Post-Tib Tendonitis:
The treatment
for Post-Tib Tendonitis focuses on reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and
promoting healing. A comprehensive approach may include the following:
- Rest: Avoiding activities
that worsen the pain to allow the tendon time to heal.
- Compression: Using
compression bandages or wraps to help manage swelling.
- Elevation: Elevating the foot
whenever possible to reduce swelling.
- Orthotics: Custom-made or
over-the-counter shoe inserts can provide support and decrease stress on
the tendon.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing
supportive and well-fitted shoes can facilitate recovery.
- Immobilization: In severe
cases, a walking boot or cast may be necessary to immobilize the foot and
allow the tendon to heal effectively.
Implementing
these treatment strategies can significantly improve comfort and recovery for
individuals suffering from Post-Tib Tendonitis.
 Posterior
Tibial Tendonitis, commonly known as Post-Tib Tendonitis, is a condition characterized
by inflammation or irritation of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon runs
along the inner side of the ankle and foot, playing a vital role in supporting
the arch and stabilizing the foot during activities like walking and running.
Posterior
Tibial Tendonitis, commonly known as Post-Tib Tendonitis, is a condition characterized
by inflammation or irritation of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon runs
along the inner side of the ankle and foot, playing a vital role in supporting
the arch and stabilizing the foot during activities like walking and running.