Trekking is a rewarding outdoor activity that allows
individuals to explore natural landscapes while enjoying physical exercise.
However, it can also lead to various injuries due to the demanding nature of
the activity, varied terrain, and environmental conditions. Understanding
common trekking-related injuries, their causes, symptoms, and prevention
strategies is essential for a safe and enjoyable trekking experience. Here are
some of the most common trekking-related injuries:
1. Sprains and Strains
- Cause:
Uneven terrain, awkward movements, or overexertion.
- Impact:
Sprains (ligament injuries) and strains (muscle or tendon injuries) are
common among trekkers, especially when navigating rocky or steep paths.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Prevention:
Proper warm-ups, wearing supportive footwear, and strengthening leg and
ankle muscles can help prevent these injuries.
2. Blisters
- Cause:
Friction between the skin and footwear, often exacerbated by moisture.
- Impact:
Blisters typically form on the feet due to repetitive rubbing, leading to
pain and discomfort. Symptoms include raised, fluid-filled areas on the
skin.
- Prevention:
Wearing well-fitted shoes, moisture-wicking socks, and using blister
prevention products (like blister pads or tape) can help reduce the risk
of blisters.
3. Knee Injuries
- Cause:
Strenuous downhill trekking, uneven surfaces, or overuse.
- Impact:
Trekking can place significant strain on the knees, leading to injuries
such as patellar tendinitis or IT band syndrome. Symptoms may include knee
pain, swelling, and difficulty with movement.
- Prevention:
Strengthening the muscles around the knee, using proper trekking
techniques, and wearing knee supports can help prevent knee injuries.
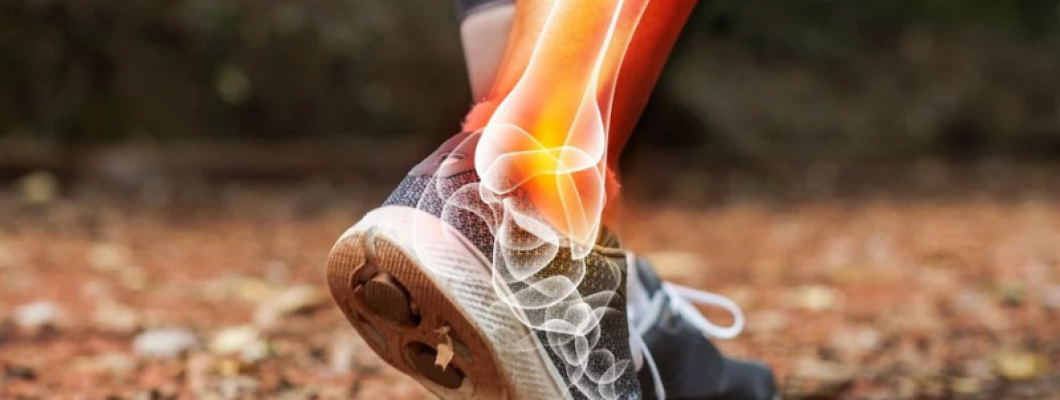
4. Ankle Injuries
- Cause:
Twisting or rolling the ankle while navigating rocky or uneven terrain.
- Impact:
Ankle sprains are common in trekking, leading to pain, swelling, and
limited mobility. Symptoms may worsen with activity.
- Prevention:
Wearing sturdy, supportive footwear, being cautious on uneven ground, and
strengthening ankle muscles can help prevent ankle injuries.
5. Heat Exhaustion and Heat Stroke
- Cause:
Trekking in high temperatures without adequate hydration or rest.
- Impact:
Prolonged exposure to heat can lead to heat exhaustion or heat stroke,
characterized by symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, headaches, and
extreme fatigue.
- Prevention:
Staying hydrated, taking regular breaks, wearing lightweight clothing, and
avoiding strenuous activity during peak heat hours can help prevent
heat-related illnesses.
6. Dehydration
- Cause:
Inadequate fluid intake during trekking.
- Impact:
Dehydration can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, headache, and
decreased performance. Severe dehydration can have serious health
implications.
- Prevention:
Carrying sufficient water, regularly drinking fluids, and consuming
electrolyte-rich beverages can help prevent dehydration.
7. Altitude Sickness
- Cause:
Rapid ascent to high altitudes without proper acclimatization.
- Impact:
Altitude sickness (acute mountain sickness) can occur at elevations above
8,000 feet and may cause symptoms such as headaches, nausea, dizziness,
and fatigue.
- Prevention:
Ascending gradually, allowing for acclimatization, and staying hydrated
can help reduce the risk of altitude sickness.
8. Sunburn and Skin Injuries
- Cause:
Prolonged exposure to sunlight without adequate protection.
- Impact:
Sunburn can lead to painful, red skin, and increase the risk of skin
cancer. Additionally, cuts and scrapes can occur from falls or rough
terrain.
- Prevention:
Applying sunscreen, wearing protective clothing and hats, and being
cautious in rugged environments can help reduce the risk of sunburn and
skin injuries.
9. Back Injuries
- Cause:
Poor lifting techniques or carrying heavy backpacks.
- Impact:
Trekking with a heavy pack can lead to back strain or injury, resulting in
pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving.
- Prevention:
Using proper lifting techniques, distributing weight evenly in the
backpack, and strengthening core muscles can help prevent back injuries.
10. Frostbite and Hypothermia
- Cause:
Exposure to cold temperatures without proper clothing.
- Impact:
Trekking in cold, wet conditions can lead to frostbite (damage to skin and
underlying tissue) or hypothermia (dangerously low body temperature).
Symptoms may include shivering, confusion, and numbness in extremities.
- Prevention:
Wearing appropriate layered clothing, staying dry, and taking regular
breaks to warm up can help prevent cold-related injuries.



2 Comment(s)
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/acapulco-gold-strain/" rel="dofollow">Acapulco Gold Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/afghani-strain/" rel="dofollow">Afghani strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/ak-47-strain/" rel="dofollow">AK 47 Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/amnesia-haze-strain/" rel="dofollow">Amnesia Haze Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/blue-gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blue Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/blueberry-muffin-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Muffin Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/bubblegum-popperz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Bubblegum Popperz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/chemdawg-strain/" rel="dofollow">Chemdawg Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/diamond-dust-strain/" rel="dofollow">Diamond Dust Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/gary-payton-strain/" rel="dofollow">Gary Payton Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/miracle-alien-cookies-strain/" rel="dofollow">Miracle Alien Cookies Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/og-kush/" rel="dofollow">OG Kush</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/permanent-marker-strain/" rel="dofollow">Permanent Marker Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/zoapscotti-strain/" rel="dofollow">Zoapscotti Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/blueberry-oil/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/co%e2%82%82-extract-oil/" rel="dofollow">CO₂ Extract Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/delta-8-distillate/" rel="dofollow">Delta 8 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/d9-distillate/" rel="dofollow">Delta 9 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/delta-10-distillate/" rel="dofollow">DELTA-10 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/hhc-distillate/" rel="dofollow">HHC Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/live-resin-oil/" rel="dofollow">Live Resin Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/purple-punch-oil/" rel="dofollow">Purple Punch oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/raw-pure-thc-oil/" rel="dofollow">Raw (Pure) THC Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/rick-simpson-oil/" rel="dofollow">Rick Simpson Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thc-clear-distillate/" rel="dofollow">THC Clear Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thc-d9-syrup/" rel="dofollow">THC Delta 9 Syrup</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/star-killer-oil/" rel="dofollow">THC Star Killer Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thca-distillate/" rel="dofollow">THCA Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thcp-distillate-oil/" rel="dofollow">THCP Distillate Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/whole-melt-extracts-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Whole Melt Extracts 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/tre-house-hhc-live-resin-disposable-vape-pens-2grams/" rel="dofollow">Tre House HHC Live Resin Disposable Vape Pens (2grams)</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/the-wizard-of-terps-1ml-syringe/" rel="dofollow">The Wizard Of Terps 1ml Syringe</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/ruby-carts-disposable-vape-pen/" rel="dofollow">Ruby Carts Disposable Vape Pen</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/potent-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Potent disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/packwoods-x-runtz/" rel="dofollow">Packwoods x Runtz</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/ace-ultra-premium-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Ace Ultra Premium Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/backpackboyz-carts/" rel="dofollow">Backpackboyz Carts</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/baked-bar-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Baked Bar 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/burst-2g-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">Burst 2g Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/cali-company-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">Cali Company Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/choice-lab-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Choice Lab 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/clean-carts-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Clean Carts 2G Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/cookies-1g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Cookies 1g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/family-high-range/" rel="dofollow">Family High Range</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/favorites-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Favorites 2G Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/gassed-up-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Gassed Up 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/jeeter-juice-carts/" rel="dofollow">Jeeter Juice Carts</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/jungle-boys-vape/" rel="dofollow">Jungle Boys Vape</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/seedless-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Seedless Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/apple-fritter-strain/" rel="dofollow">Apple Fritter Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/biscotti-strain/" rel="dofollow">Biscotti Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/blueberry-zkittlez-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cheese-kush/" rel="dofollow">Cheese strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/gg4-strain/" rel="dofollow">GG4 Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/godfather-og-strain/" rel="dofollow">Godfather OG Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/stardawg-strain/" rel="dofollow">Stardawg Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/super-lemon-cherry-strain/" rel="dofollow">Super Lemon Cherry Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/wedding-cake-strain-2/" rel="dofollow">Wedding Cake Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/white-widow-strain/" rel="dofollow">White Widow Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/girl-scout-cookies/" rel="dofollow">Girl Scout Cookies</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/granddaddy-purple-gdp-strain/" rel="dofollow">Granddaddy Purple Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/ice-cream-cake-strain/" rel="dofollow">Ice Cream Cake Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/master-kush/" rel="dofollow">Master Kush</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/northern-lights/" rel="dofollow">Northern Lights strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/skywalker-kush/" rel="dofollow">Skywalker Kush</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/watermelon-gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Watermelon Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/zeus-og-strain/" rel="dofollow">Zeus OG Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/amnesia-haze/" rel="dofollow">Amnesia Haze</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/bruce-banner-strain/" rel="dofollow">Bruce Banner Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/durban-poison/" rel="dofollow">Durban Poison</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/guava-weed-strain/" rel="dofollow">Guava Weed Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/maui-wowie-strain/" rel="dofollow">Maui Wowie Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/mimosa-strain/" rel="dofollow">Mimosa Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/sour-diesel-strain/" rel="dofollow">Sour Diesel Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/super-silver-haze/" rel="dofollow">Super Silver Haze</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/big-chief-carts/" rel="dofollow">Big Chief Carts</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cake-vape-pen/" rel="dofollow">CAKE VAPE PEN</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cali-company-1g-vapes/" rel="dofollow">Cali Company 1g Vapes</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/dope-disposable-vape-pens/" rel="dofollow">Dope Disposable Vape Pens</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/england-trap-1g-vape/" rel="dofollow">England Trap 1g Vape</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/expensive-sht-vapes/" rel="dofollow">Expensive Sh*t Vapes</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/fryd-vape/" rel="dofollow">FRYD VAPE</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/muha-meds-vape/" rel="dofollow">Muha Meds Vape</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/packman-vape/" rel="dofollow">PACKMAN VAPE</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/packwoods-vape/" rel="dofollow">PACKWOODS VAPE</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cali-plates-hash/" rel="dofollow">Cali Plates Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/fly-farm-hash/" rel="dofollow">FLY FARM HASH</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/16147/" rel="dofollow">Kilogrammes Farm Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/la-mousse-hash-review/" rel="dofollow">La Mousse Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/lemon-haze-hash/" rel="dofollow">LEMON HAZE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/static-room-hash/" rel="dofollow">Static Room Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/super-pollen-hash/" rel="dofollow">Super Pollen Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/tangie-hash/" rel="dofollow">TANGIE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/wazabi-hash/" rel="dofollow">WAZABI HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/alien-og-hash/" rel="dofollow">Alien OG hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/cali-plates-hash/" rel="dofollow">Cali Plates Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/fly-farm-hash/" rel="dofollow">FLY FARM HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/kilogrammes-farm-hash/" rel="dofollow">Kilogrammes Farm Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/la-mousse-hash/" rel="dofollow">La Mousse Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/lemon-haze-hash/" rel="dofollow">LEMON HAZE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/pollen-hash/" rel="dofollow">POLLEN HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/static-room-hash/" rel="dofollow">Static Room Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/tangie-hash/" rel="dofollow">TANGIE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/wazabi-hash/" rel="dofollow">WAZABI HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/41-unicornz-strain/" rel="dofollow">41 Unicornz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/apple-fritter-strain/" rel="dofollow">Apple Fritter Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/biscotti-strain/" rel="dofollow">Biscotti Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/blue-gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blue Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/blueberry-muffin-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Muffin Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/bubblegum-popperz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Bubblegum Popperz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/gary-payton-strain/" rel="dofollow">Gary Payton Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/hella-jelly-strain/" rel="dofollow">Hella Jelly Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/kosher-kush-strain/" rel="dofollow">Kosher Kush Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/lava-cake-strain/" rel="dofollow">Lava Cake Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/miracle-alien-cookies-strain/" rel="dofollow">Miracle Alien Cookies Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/moonrock-pre-roll/" rel="dofollow">Moonrock Pre Roll</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/og-kush/" rel="dofollow">OG Kush</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/tropical-runtz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Tropical runtz strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/watermelon-runtz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Watermelon Runtz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/backpackboyz-cart/" rel="dofollow">Backpackboyz Cart</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/baked-bar-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Baked Bar Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/cali-plug-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">Cali Plug Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/clean-carts-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Clean Carts 2G Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/d9-distillate/" rel="dofollow">D9 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/elites-switch-1g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Elites Switch 1g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/expensive-shit-1g-vape/" rel="dofollow">Expensive Shit 1g Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/fryd-donuts-disposable-2g/" rel="dofollow">Fryd Donuts Disposable (2g)</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/gassed-up-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Gassed Up 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/jungle-boys-vape/" rel="dofollow">Jungle Boys Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/kushy-punch-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Kushy Punch Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/melt-x-packwoods/" rel="dofollow">Melt X Packwoods</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/packspod-vape/" rel="dofollow">Packspod Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/the-cali-company-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">The Cali company disposable vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/tyson-pod-1000mg/" rel="dofollow">Tyson Pod 1000mg</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-the-10-10-boys-2g-disposable-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy THE 10/10 BOYS 2G DISPOSABLE online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-co2-extract-oil-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy CO2 Extract Oil Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-deep-sleep-thc-tincture-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Deep Sleep THC Tincture Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-thc-mood-magic-tincture-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy THC Mood Magic Tincture online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-atlrx-delta-8-thc-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy ATLRx Delta 8 THC Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-revival-watermelon-thc-tincture-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Revival Watermelon THC Tincture online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-diamond-extracts-thc-tinctures-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Diamond Extracts THC Tinctures Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thc-p-vape-cartridge/" rel "dofollow">THC-P Vape Cartridge</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thca-disposable-2-gram-gourmet-desserts/" rel "dofollow">THCA Disposable 2 Gram – Gourmet Desserts</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/blazed-7-gram-thca-delta-9b-disposable-vape/" rel "dofollow">Blazed 7 Gram THCA + Delta 9B Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/7-gram-thca-high-thc-p-disposable-vape-limited-series/" rel "dofollow">7 Gram THCA + High THC-P Disposable Vape – Limited Series</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/knockout-blend-live-resin-disposable-2-gram/" rel "dofollow">Knockout Blend Live Resin Disposable – 2 Gram</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/phc-disposable-vape-2-gram/" rel "dofollow">PHC Disposable Vape – 2 Gram</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/hhc-disposable-vape-2-gram-tre-house/" rel "dofollow">HHC Disposable Vape 2 Gram – TRE House</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/live-resin-hhc-p-disposable-vape-delta-extrax/" rel "dofollow">Live Resin HHC-P Disposable Vape – Delta Extrax</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thc-jd-3-gram-disposable-thins-delta-extrax/" rel "dofollow">THC-JD 3 Gram Disposable Thins – Delta Extrax</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thca-delta-9p-3-gram-disposable-blazed/" rel "dofollow">THCA + Delta 9P 3 Gram Disposable – Blazed</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/5-gram-thca-thcm-disposable-vape-exclusive-series/" rel "dofollow">5 Gram THCA + THCM Disposable Vape – Exclusive Series</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/?post_type=product&p=519&preview=true" rel "dofollow">2 Gram THCA Disposable Vapes – Live Rosin</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thca-vape-cartridge-exotic-kush-live-rosin/" rel "dofollow">THCA Vape Cartridge Exotic Kush – Live Rosin</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/1-gram-thca-disposable-vapes-live-rosin/" rel "dofollow">1 Gram THCA Disposable Vapes – Live Rosin</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/2g-thca-disposable-vapes-minnesota-fire/" rel "dofollow">2G THCA Disposable Vapes – Minnesota Fire</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thc-vape-juice-wedding-cake/" rel "dofollow">THC Vape Juice Wedding Cake</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-urb-disposable-vape/" rel "dofollow">Buy URB Disposable vape</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-xtra-disposables-vape-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Xtra Disposables vape online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-runtz-disposable-vape-pen/" rel "dofollow">Buy RUNTZ DISPOSABLE VAPE PEN</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-dmt-vape-pens/" rel "dofollow">buy Dmt Vape Pens</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/rainbows-and-cherries-live-budder/" rel "dofollow">Rainbows and Cherries Live Budder</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/2-5g-citrus-mac-live-budder/" rel "dofollow">2.5g Citrus MAC Live Budder</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/1g-peking-duck-live-sugar/" rel "dofollow">1g Peking Duck Live Sugar</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/30ml-rest-15-tincture/" rel "dofollow">30ml Rest 1:5 Tincture</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/1g-face-mints-liquid-live-resin-cartridge/" rel "dofollow">1g Face Mints Liquid Live Resin Cartridge</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/acitivated-thc-distillate-strike-gold/" rel="dofollow">Activated THC distillate Strike gold</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/good-trip-mushroom-chocolate-bars/" rel="dofollow">Good Trip Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/fusion-mushroom-chocolate-bars/" rel="dofollow">Fusion Mushroom Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-acid/" rel="dofollow">Lsd (acid)</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-gel/" rel="dofollow">Lsd Gel Tabs</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-sheets/" rel="dofollow">LSD SHEETS</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd/" rel="dofollow">Lsd</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/green-hulk-250mg-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Green Hulk (MDMA)</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/white-yellow-technogym/" rel="dofollow">White & Yellow Technogym</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/orange-sprite-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Orange Sprite MDMA Pills</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/red-bull-258mg-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Red Bull Pills (MDMA)</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/orange-trump-260mg-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Orange Trump 260mg MDMA</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-mushroom-chocolate-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Mushroom Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-raspberry-dark-chocolate-shroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Raspberry Dark Shroom Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-tagalongs-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Tagalongs Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-vanilla-biscuit/" rel="dofollow"></a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-vanilla-biscuit/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Vanilla Biscuit</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-mushroom-bars-cookies-and-cream/" rel="dofollow">One Up Psilocybin Mushroom Cookies and Cream</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-mushroom-bars-do-si-dos/" rel="dofollow">One Up Do-Si-Dos Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-samoas-mushroom-bar/" rel="dofollow">One Up Samoas Mushroom Bar</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-strawberries-and-cream-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Strawberries and Cream Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-thin-mints-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Thin Mints Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-almond-crush-chocolate-bar/" rel="dofollow">One Up Multiverse Almond Crush Chocolate Bar</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-blueberry-yogurt/" rel="dofollow">One Up Multiverse Blueberry Yogurt</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-oreo-milkshake/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Oreo Milkshake</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-matcha-milk-tea/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Matcha Milk Tea</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-strawberry-shortcake/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Strawberry Shortcake</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-psychedelic-chocolate-bar/" rel="dofollow">One Up Psilocybin Chocolate Bar</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-trefoils-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Trefoils Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/filthy-laboratory/" rel="dofollow">FILTHY LABORATORY</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/flavrx-cartridge/" rel="dofollow">FlavRX Cartridge</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/chronopoly-carts/" rel="dofollow">Chronopoly Carts</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/big-chief-extracts/" rel="dofollow">Big chief extracts</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/exxus-snap/" rel="dofollow">Exxus Snap</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/stiiizys-starter-kit/" rel="dofollow">Stiiizy Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/exotic-carts/" rel="dofollow">EXOTIC CARTS</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/brass-knuckles-cartridges/" rel="dofollow">Brass Knuckles Cartridges</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/5-me0-dmt/" rel="dofollow">5-Me0-DMT</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/albino-penis-envy-grow-kits/" rel="dofollow">albino penis envy grow kits</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/blue-oyster-mushrooms/" rel="dofollow">blue Oyster Mushroom</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lions-mane/" rel="dofollow">Lion’s Mane</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/dmt/" rel="dofollow">DMT</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/ecstasy-molly/" rel="dofollow">Ecstasy Pills</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/dmt-vape-pen-and-cartridges/" rel="dofollow">DMT VAPE PEN</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/5-meo-dmt/" rel="dofollow">5-MeO DMT</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-liquid/" rel="dofollow">Liquid LSD</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/gel-tabs-lsd-300ug/" rel="dofollow">Gel tabs lsd</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-tabs-250ug/" rel="dofollow">LSD Tabs</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/mdma-crystal/" rel="dofollow">MDMA Crystal</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/psilocybe-azurescens-dried-shrooms/" rel="dofollow">Psilocybe Azurescens mushrooms</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/golden-teacher-mushrooms/" rel="dofollow">Golden Teacher Mushrooms</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/true-albino-teacher-mushroom/" rel="dofollow">True Albino Teacher</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/psilocybe-cyanescens-dried-shrooms/" rel="dofollow">Psilocybe Cyanescens</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/penis-envy/" rel="dofollow">Penis Envy</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/great-white-monster-psilocybe-cubensis/" rel="dofollow">Great White Monster-Psilocybe Cubensis</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/big-daddy-psilocybe-cubensis/" rel="dofollow">Big Daddy Psilocybe Cubensis</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/avery-albino-magic-mushroom/" rel="dofollow">Avery Albino Magic Mushroom</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/albino-cambodians-psilocybe-cubensis/" rel="dofollow">Albino Cambodians Psilocybe Cubensis</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/albino-a-magic-mushroom-dried-shrooms/" rel="dofollow">Albino A+ Magic Mushroom</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/acapulco-gold-strain/" rel="dofollow">Acapulco Gold Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/afghani-strain/" rel="dofollow">Afghani strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/ak-47-strain/" rel="dofollow">AK 47 Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/amnesia-haze-strain/" rel="dofollow">Amnesia Haze Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/blue-gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blue Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/blueberry-muffin-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Muffin Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/bubblegum-popperz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Bubblegum Popperz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/chemdawg-strain/" rel="dofollow">Chemdawg Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/diamond-dust-strain/" rel="dofollow">Diamond Dust Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/gary-payton-strain/" rel="dofollow">Gary Payton Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/miracle-alien-cookies-strain/" rel="dofollow">Miracle Alien Cookies Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/og-kush/" rel="dofollow">OG Kush</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/permanent-marker-strain/" rel="dofollow">Permanent Marker Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/zoapscotti-strain/" rel="dofollow">Zoapscotti Strain</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/blueberry-oil/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/co%e2%82%82-extract-oil/" rel="dofollow">CO₂ Extract Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/delta-8-distillate/" rel="dofollow">Delta 8 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/d9-distillate/" rel="dofollow">Delta 9 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/delta-10-distillate/" rel="dofollow">DELTA-10 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/hhc-distillate/" rel="dofollow">HHC Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/live-resin-oil/" rel="dofollow">Live Resin Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/purple-punch-oil/" rel="dofollow">Purple Punch oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/raw-pure-thc-oil/" rel="dofollow">Raw (Pure) THC Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/rick-simpson-oil/" rel="dofollow">Rick Simpson Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thc-clear-distillate/" rel="dofollow">THC Clear Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thc-d9-syrup/" rel="dofollow">THC Delta 9 Syrup</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/star-killer-oil/" rel="dofollow">THC Star Killer Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thca-distillate/" rel="dofollow">THCA Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/thcp-distillate-oil/" rel="dofollow">THCP Distillate Oil</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/whole-melt-extracts-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Whole Melt Extracts 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/tre-house-hhc-live-resin-disposable-vape-pens-2grams/" rel="dofollow">Tre House HHC Live Resin Disposable Vape Pens (2grams)</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/the-wizard-of-terps-1ml-syringe/" rel="dofollow">The Wizard Of Terps 1ml Syringe</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/ruby-carts-disposable-vape-pen/" rel="dofollow">Ruby Carts Disposable Vape Pen</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/potent-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Potent disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/packwoods-x-runtz/" rel="dofollow">Packwoods x Runtz</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/ace-ultra-premium-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Ace Ultra Premium Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/backpackboyz-carts/" rel="dofollow">Backpackboyz Carts</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/baked-bar-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Baked Bar 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/burst-2g-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">Burst 2g Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/cali-company-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">Cali Company Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/choice-lab-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Choice Lab 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/clean-carts-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Clean Carts 2G Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/cookies-1g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Cookies 1g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/family-high-range/" rel="dofollow">Family High Range</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/favorites-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Favorites 2G Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/gassed-up-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Gassed Up 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/jeeter-juice-carts/" rel="dofollow">Jeeter Juice Carts</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/jungle-boys-vape/" rel="dofollow">Jungle Boys Vape</a>
<ahref="https://disposablecartsuk.com/product/seedless-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Seedless Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/apple-fritter-strain/" rel="dofollow">Apple Fritter Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/biscotti-strain/" rel="dofollow">Biscotti Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/blueberry-zkittlez-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cheese-kush/" rel="dofollow">Cheese strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/gg4-strain/" rel="dofollow">GG4 Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/godfather-og-strain/" rel="dofollow">Godfather OG Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/stardawg-strain/" rel="dofollow">Stardawg Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/super-lemon-cherry-strain/" rel="dofollow">Super Lemon Cherry Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/wedding-cake-strain-2/" rel="dofollow">Wedding Cake Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/white-widow-strain/" rel="dofollow">White Widow Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/girl-scout-cookies/" rel="dofollow">Girl Scout Cookies</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/granddaddy-purple-gdp-strain/" rel="dofollow">Granddaddy Purple Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/ice-cream-cake-strain/" rel="dofollow">Ice Cream Cake Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/master-kush/" rel="dofollow">Master Kush</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/northern-lights/" rel="dofollow">Northern Lights strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/skywalker-kush/" rel="dofollow">Skywalker Kush</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/watermelon-gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Watermelon Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/zeus-og-strain/" rel="dofollow">Zeus OG Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/amnesia-haze/" rel="dofollow">Amnesia Haze</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/bruce-banner-strain/" rel="dofollow">Bruce Banner Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/durban-poison/" rel="dofollow">Durban Poison</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/guava-weed-strain/" rel="dofollow">Guava Weed Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/maui-wowie-strain/" rel="dofollow">Maui Wowie Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/mimosa-strain/" rel="dofollow">Mimosa Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/sour-diesel-strain/" rel="dofollow">Sour Diesel Strain</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/super-silver-haze/" rel="dofollow">Super Silver Haze</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/big-chief-carts/" rel="dofollow">Big Chief Carts</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cake-vape-pen/" rel="dofollow">CAKE VAPE PEN</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cali-company-1g-vapes/" rel="dofollow">Cali Company 1g Vapes</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/dope-disposable-vape-pens/" rel="dofollow">Dope Disposable Vape Pens</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/england-trap-1g-vape/" rel="dofollow">England Trap 1g Vape</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/expensive-sht-vapes/" rel="dofollow">Expensive Sh*t Vapes</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/fryd-vape/" rel="dofollow">FRYD VAPE</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/muha-meds-vape/" rel="dofollow">Muha Meds Vape</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/packman-vape/" rel="dofollow">PACKMAN VAPE</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/packwoods-vape/" rel="dofollow">PACKWOODS VAPE</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/cali-plates-hash/" rel="dofollow">Cali Plates Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/fly-farm-hash/" rel="dofollow">FLY FARM HASH</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/16147/" rel="dofollow">Kilogrammes Farm Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/la-mousse-hash-review/" rel="dofollow">La Mousse Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/lemon-haze-hash/" rel="dofollow">LEMON HAZE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/static-room-hash/" rel="dofollow">Static Room Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/super-pollen-hash/" rel="dofollow">Super Pollen Hash</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/tangie-hash/" rel="dofollow">TANGIE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://englandtrap.com/product/wazabi-hash/" rel="dofollow">WAZABI HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/alien-og-hash/" rel="dofollow">Alien OG hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/cali-plates-hash/" rel="dofollow">Cali Plates Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/fly-farm-hash/" rel="dofollow">FLY FARM HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/kilogrammes-farm-hash/" rel="dofollow">Kilogrammes Farm Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/la-mousse-hash/" rel="dofollow">La Mousse Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/lemon-haze-hash/" rel="dofollow">LEMON HAZE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/pollen-hash/" rel="dofollow">POLLEN HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/static-room-hash/" rel="dofollow">Static Room Hash</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/tangie-hash/" rel="dofollow">TANGIE HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/wazabi-hash/" rel="dofollow">WAZABI HASH</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/41-unicornz-strain/" rel="dofollow">41 Unicornz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/apple-fritter-strain/" rel="dofollow">Apple Fritter Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/biscotti-strain/" rel="dofollow">Biscotti Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/blue-gelato-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blue Gelato Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/blueberry-muffin-strain/" rel="dofollow">Blueberry Muffin Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/bubblegum-popperz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Bubblegum Popperz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/gary-payton-strain/" rel="dofollow">Gary Payton Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/hella-jelly-strain/" rel="dofollow">Hella Jelly Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/kosher-kush-strain/" rel="dofollow">Kosher Kush Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/lava-cake-strain/" rel="dofollow">Lava Cake Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/miracle-alien-cookies-strain/" rel="dofollow">Miracle Alien Cookies Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/moonrock-pre-roll/" rel="dofollow">Moonrock Pre Roll</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/og-kush/" rel="dofollow">OG Kush</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/tropical-runtz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Tropical runtz strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/watermelon-runtz-strain/" rel="dofollow">Watermelon Runtz Strain</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/backpackboyz-cart/" rel="dofollow">Backpackboyz Cart</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/baked-bar-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Baked Bar Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/cali-plug-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">Cali Plug Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/clean-carts-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Clean Carts 2G Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/d9-distillate/" rel="dofollow">D9 Distillate</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/elites-switch-1g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Elites Switch 1g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/expensive-shit-1g-vape/" rel="dofollow">Expensive Shit 1g Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/fryd-donuts-disposable-2g/" rel="dofollow">Fryd Donuts Disposable (2g)</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/gassed-up-2g-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Gassed Up 2g Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/jungle-boys-vape/" rel="dofollow">Jungle Boys Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/kushy-punch-disposable/" rel="dofollow">Kushy Punch Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/melt-x-packwoods/" rel="dofollow">Melt X Packwoods</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/packspod-vape/" rel="dofollow">Packspod Vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/the-cali-company-disposable-vape/" rel="dofollow">The Cali company disposable vape</a>
<ahref="https://hashclinicc.com/product/tyson-pod-1000mg/" rel="dofollow">Tyson Pod 1000mg</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-the-10-10-boys-2g-disposable-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy THE 10/10 BOYS 2G DISPOSABLE online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-co2-extract-oil-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy CO2 Extract Oil Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-deep-sleep-thc-tincture-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Deep Sleep THC Tincture Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-thc-mood-magic-tincture-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy THC Mood Magic Tincture online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-atlrx-delta-8-thc-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy ATLRx Delta 8 THC Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-revival-watermelon-thc-tincture-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Revival Watermelon THC Tincture online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-diamond-extracts-thc-tinctures-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Diamond Extracts THC Tinctures Online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thc-p-vape-cartridge/" rel "dofollow">THC-P Vape Cartridge</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thca-disposable-2-gram-gourmet-desserts/" rel "dofollow">THCA Disposable 2 Gram – Gourmet Desserts</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/blazed-7-gram-thca-delta-9b-disposable-vape/" rel "dofollow">Blazed 7 Gram THCA + Delta 9B Disposable Vape</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/7-gram-thca-high-thc-p-disposable-vape-limited-series/" rel "dofollow">7 Gram THCA + High THC-P Disposable Vape – Limited Series</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/knockout-blend-live-resin-disposable-2-gram/" rel "dofollow">Knockout Blend Live Resin Disposable – 2 Gram</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/phc-disposable-vape-2-gram/" rel "dofollow">PHC Disposable Vape – 2 Gram</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/hhc-disposable-vape-2-gram-tre-house/" rel "dofollow">HHC Disposable Vape 2 Gram – TRE House</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/live-resin-hhc-p-disposable-vape-delta-extrax/" rel "dofollow">Live Resin HHC-P Disposable Vape – Delta Extrax</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thc-jd-3-gram-disposable-thins-delta-extrax/" rel "dofollow">THC-JD 3 Gram Disposable Thins – Delta Extrax</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thca-delta-9p-3-gram-disposable-blazed/" rel "dofollow">THCA + Delta 9P 3 Gram Disposable – Blazed</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/5-gram-thca-thcm-disposable-vape-exclusive-series/" rel "dofollow">5 Gram THCA + THCM Disposable Vape – Exclusive Series</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/?post_type=product&p=519&preview=true" rel "dofollow">2 Gram THCA Disposable Vapes – Live Rosin</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thca-vape-cartridge-exotic-kush-live-rosin/" rel "dofollow">THCA Vape Cartridge Exotic Kush – Live Rosin</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/1-gram-thca-disposable-vapes-live-rosin/" rel "dofollow">1 Gram THCA Disposable Vapes – Live Rosin</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/2g-thca-disposable-vapes-minnesota-fire/" rel "dofollow">2G THCA Disposable Vapes – Minnesota Fire</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/thc-vape-juice-wedding-cake/" rel "dofollow">THC Vape Juice Wedding Cake</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-urb-disposable-vape/" rel "dofollow">Buy URB Disposable vape</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-xtra-disposables-vape-online/" rel "dofollow">Buy Xtra Disposables vape online</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-runtz-disposable-vape-pen/" rel "dofollow">Buy RUNTZ DISPOSABLE VAPE PEN</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/buy-dmt-vape-pens/" rel "dofollow">buy Dmt Vape Pens</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/rainbows-and-cherries-live-budder/" rel "dofollow">Rainbows and Cherries Live Budder</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/2-5g-citrus-mac-live-budder/" rel "dofollow">2.5g Citrus MAC Live Budder</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/1g-peking-duck-live-sugar/" rel "dofollow">1g Peking Duck Live Sugar</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/30ml-rest-15-tincture/" rel "dofollow">30ml Rest 1:5 Tincture</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/1g-face-mints-liquid-live-resin-cartridge/" rel "dofollow">1g Face Mints Liquid Live Resin Cartridge</a>
<ahref="https://vapestorecart.com/product/acitivated-thc-distillate-strike-gold/" rel="dofollow">Activated THC distillate Strike gold</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/good-trip-mushroom-chocolate-bars/" rel="dofollow">Good Trip Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/fusion-mushroom-chocolate-bars/" rel="dofollow">Fusion Mushroom Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-acid/" rel="dofollow">Lsd (acid)</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-gel/" rel="dofollow">Lsd Gel Tabs</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-sheets/" rel="dofollow">LSD SHEETS</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd/" rel="dofollow">Lsd</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/green-hulk-250mg-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Green Hulk (MDMA)</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/white-yellow-technogym/" rel="dofollow">White & Yellow Technogym</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/orange-sprite-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Orange Sprite MDMA Pills</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/red-bull-258mg-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Red Bull Pills (MDMA)</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/orange-trump-260mg-mdma/" rel="dofollow">Orange Trump 260mg MDMA</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-mushroom-chocolate-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Mushroom Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-raspberry-dark-chocolate-shroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Raspberry Dark Shroom Chocolate Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-tagalongs-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Tagalongs Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-vanilla-biscuit/" rel="dofollow"></a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-vanilla-biscuit/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Vanilla Biscuit</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-mushroom-bars-cookies-and-cream/" rel="dofollow">One Up Psilocybin Mushroom Cookies and Cream</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-mushroom-bars-do-si-dos/" rel="dofollow">One Up Do-Si-Dos Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-samoas-mushroom-bar/" rel="dofollow">One Up Samoas Mushroom Bar</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-strawberries-and-cream-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Strawberries and Cream Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-thin-mints-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Thin Mints Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-almond-crush-chocolate-bar/" rel="dofollow">One Up Multiverse Almond Crush Chocolate Bar</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-blueberry-yogurt/" rel="dofollow">One Up Multiverse Blueberry Yogurt</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-oreo-milkshake/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Oreo Milkshake</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-matcha-milk-tea/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Matcha Milk Tea</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-multiverse-strawberry-shortcake/" rel="dofollow">One up Multiverse Strawberry Shortcake</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-psychedelic-chocolate-bar/" rel="dofollow">One Up Psilocybin Chocolate Bar</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/one-up-trefoils-mushroom-bars/" rel="dofollow">One Up Trefoils Mushroom Bars</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/filthy-laboratory/" rel="dofollow">FILTHY LABORATORY</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/flavrx-cartridge/" rel="dofollow">FlavRX Cartridge</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/chronopoly-carts/" rel="dofollow">Chronopoly Carts</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/big-chief-extracts/" rel="dofollow">Big chief extracts</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/exxus-snap/" rel="dofollow">Exxus Snap</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/stiiizys-starter-kit/" rel="dofollow">Stiiizy Disposable</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/exotic-carts/" rel="dofollow">EXOTIC CARTS</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/brass-knuckles-cartridges/" rel="dofollow">Brass Knuckles Cartridges</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/5-me0-dmt/" rel="dofollow">5-Me0-DMT</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/albino-penis-envy-grow-kits/" rel="dofollow">albino penis envy grow kits</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/blue-oyster-mushrooms/" rel="dofollow">blue Oyster Mushroom</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lions-mane/" rel="dofollow">Lion’s Mane</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/dmt/" rel="dofollow">DMT</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/ecstasy-molly/" rel="dofollow">Ecstasy Pills</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/dmt-vape-pen-and-cartridges/" rel="dofollow">DMT VAPE PEN</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/5-meo-dmt/" rel="dofollow">5-MeO DMT</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-liquid/" rel="dofollow">Liquid LSD</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/gel-tabs-lsd-300ug/" rel="dofollow">Gel tabs lsd</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/lsd-tabs-250ug/" rel="dofollow">LSD Tabs</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/mdma-crystal/" rel="dofollow">MDMA Crystal</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/psilocybe-azurescens-dried-shrooms/" rel="dofollow">Psilocybe Azurescens mushrooms</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/golden-teacher-mushrooms/" rel="dofollow">Golden Teacher Mushrooms</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/true-albino-teacher-mushroom/" rel="dofollow">True Albino Teacher</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/psilocybe-cyanescens-dried-shrooms/" rel="dofollow">Psilocybe Cyanescens</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/penis-envy/" rel="dofollow">Penis Envy</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/great-white-monster-psilocybe-cubensis/" rel="dofollow">Great White Monster-Psilocybe Cubensis</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/big-daddy-psilocybe-cubensis/" rel="dofollow">Big Daddy Psilocybe Cubensis</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/avery-albino-magic-mushroom/" rel="dofollow">Avery Albino Magic Mushroom</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/albino-cambodians-psilocybe-cubensis/" rel="dofollow">Albino Cambodians Psilocybe Cubensis</a>
<ahref="https://psychedelictripgateway.com/product/albino-a-magic-mushroom-dried-shrooms/" rel="dofollow">Albino A+ Magic Mushroom</a>
Leave a Comment